Single glazing is a single layer of glass and isn't effective in reducing the transfer of heat, light, sound, or U.V. It is not often used in external situations as there are more effective options.
Glass
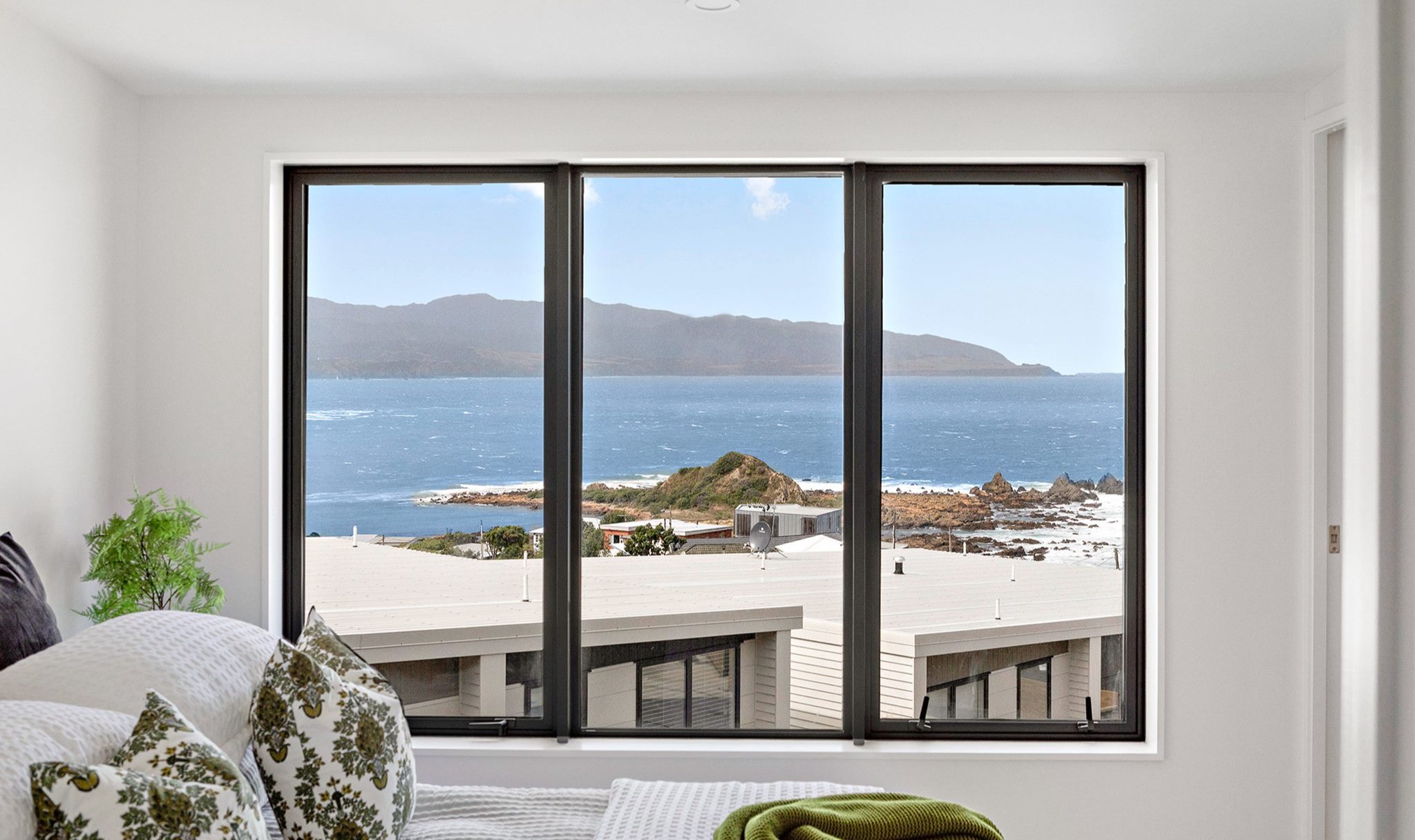

Glass plays a big role in the comfort of a space
When optimised, double glazing acts as an insulator, reduces noise, and the transfer of heat or cold from the inside to the outside and vice versa. Other types of glass such as Low-E glass can further improve the thermal efficiency of a building.
By combining different glass types and thicknesses we can help you choose a high-performance option that suits the individual needs of each project.
All glazing in UNO windows and doors comply with the NZ Building code NZS 4223
Double glazing is a requirement in all new build homes in New Zealand
Low-E glass increases the energy efficiency of your home
Glass types
Single glazing
Double glazing
Laminated
Low-E
Obscure
Tinted
Double glazing or an insulated glazing unit is made of two layers of glass with a sealed air space between. Performance can be optimised by selecting the correct spacer gap and types of glass.
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass with two panes held together by a clear vinyl interlayer. Laminated glass is often used for sound reduction and to reduce fading. It is also one of the most effective types of safety glass for security purposes.
Low-E glass has a coating which improves its thermal efficiency. The coating is virtually invisible but will have a positive impact on the heat transfer through the glass.
Obscure glass is used for privacy as it restricts visibility through a window. It is commonly used in areas like bathrooms.
Tinted glass can be used to reduce the glare and fading from the sun or as an aesthetic feature. Grey tinted glass is common in New Zealand homes.
Glass tint colours


Still unsure about colour choices? Try out our glass and colour selector to create the perfect combo for your new windows and doors!
Energy efficient glass
Energy efficiency is a common phrase, but what does it actually mean?
If two buildings are supplied with the same amount of energy to create heat, the building that generates and retains the most heat, rather than only creating a little and then losing it, is the more energy-efficient building. If we apply this concept to windows, when heating or cooling a home, some of that energy is lost through your windows. By choosing an energy-efficient glass type, the energy lost through your windows is reduced.
Low emissivity or Low-E glass is recommended to increase the energy efficiency of windows. When looking out through Low-E glass, the virtually invisible high-tech coating, lets light into your home, while reflecting heat. It improves double-glazing to further insulate your home in winter, and helps to keep your home cooler in summer. Low-E glass is available in a range of performance levels to suit your home and requirements.
In summer, Low-E glass reflects the sun’s heat is back outside, reducing internal heat gain.

During winter, Low-E glass reflects heat back into the room, so less heat is lost through the windows.
Low-E double glazing performance can be further increased with the addition of a thermal spacer and argon gas.
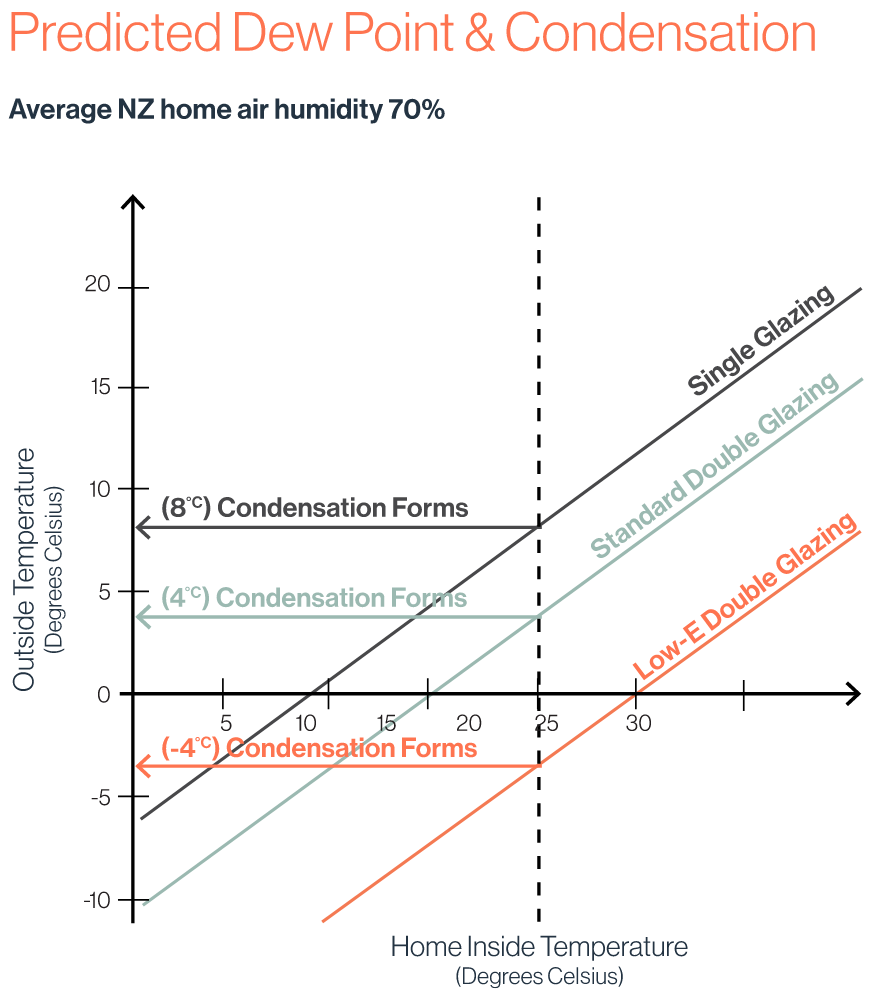
The surface temperature at which condensation begins to form is called the “dew point”. Relative humidity is a measure of the water content of the air at a given temperature. Many domestic activities, such as cooking and washing, will liberate water vapour and increase the relative humidity and thus the occurrence of condensation.
The onset of condensation on the interior glass surface can be controlled either by reducing the humidity, thereby lowering the dew point, or by raising the inside glass surface temperature. The use of Low-E glass and/or Argon Gas further enhances the U Value performance, making the inner glass warmer, and thus reducing condensation.
Double glazing vs. Low-E glass
Double glazing offers some energy efficiency when compared to single glazing, however Low-E glass can further improve the performance of the windows in your home. To learn more about the benefits of Low-E glass, check out our blog: Low-E glass and why it's perfect for winter.
Below are the four types of Low-E glass in comparison with standard double glazing. With these options, you can choose a glass that both meets your requirements and your budget. The Indicative WEERS star ratings shown are a guide and will vary with different frame types and or window/door sizes.
Energy efficiency (low > high)
WEERS rating Thermal performance using standard aluminium frame. Rating out of 6.


The benefits of choosing a high performance, energy efficient glass for your home
Lower power bills
Low-E glass has a coating which reflects the heat back from its source, either from the inside or the out and reduces the amount of energy you need to heat or cool a building internally, providing energy savings over the course of a year.
Reduced condensation
Low-E double glazing increases the internal glass surface temperature, which reduces the likelihood of condensation on the inner glass surface. Condensation is also relative to the humidity inside an area, sometimes a dehumidifier helps to reduce the humidity.
Warmer healthier home
Low-E glass reflects heat back into a room, so less heat is lost through the window. The resulting reduced condensation on the inner glass surface means your home stays drier, which in turn makes for a more healthy living environment.
Improved insulation
Low-E glass reduces heat loss and solar gain, reducing heating needs in winter and cooling requirements in summer. Better insulation makes it easier to keep temperatures constant, so the internal comfort level is increased.
Reduced fading
Low-E double glazed windows can help protect furnishings in the home from fading by reducing levels of UV light from the sun.
Choosing the right glass for your home
Depending on how many windows you have in your home, how much sun exposure you have and other factors, there are a few key things to think about when choosing your glass. There are a few main challenges that glass can create. We outline below what type of glass is best suited to minimise that particular issue.
Sound

UV / Fading

Heat gain

Light and glare

Heat loss and condensation

Safety and security

Sound
With compact housing and traffic or industrial noise, sound reduction is an important factor when choosing glass. There are a range of glass types that will reduce sound, but it does depend on the frequency and pitch of the sound as to what type of glass is most effective.
A double glazed unit has significantly better acoustic performance compared to single glazing, however, laminated glass is the most effective option.
*PSR - Perceived sound reduction % in comparison to 3mm clear float glass. Percentages vary depending on glass combinations.

UV / Fading
UV damage or fading to furnishings is something that is often thought about when selecting glass. You can reduce fading by selecting glass that reduces the UV transmission through the window.
Tinted glass is an effective option for reducing fading as the interlayer absorbs the UV light. To further reduce fading we suggest combining tinted glass with laminated glass. Reflective glass is the best to reduce fading.
*FRC = Fading reduction coefficient compared to 3mm clear float glass. Performance depends on glass combinations.

Heat gain
Heat gain from the sun is a common challenge in New Zealand homes. Double glazing can help regulate inside temperatures by reducing the heat transfer from outside.
Tinted and Low-E glass will further reduce the heat gain as they absorb solar energy.
Reflective glass is the best option to reduce solar heat gain, but it is not commonly used in homes.
*Reduced solar heat gain in comparison with clear on clear double glazing. Percentages vary depending on glass combinations.

Light and glare
The glare from the sun can be frustrating in areas exposed to the sun. Glare can be minimised by choosing glass that reduces the light transmission.
Low-E coating helps to reduce light transmission, and tinted glass will further reduce the glare. Reflective glass is the best to reduce light and glare, but it is not commonly used in homes.
*VLT% is the approximate visible light transmission. Percentages vary depending on glass combinations. Clear on clear double glazing has a VLT of approximately 80%.
Heat loss and condensation
A standard double glazed unit will effectively reduce heat loss and condensation in comparison to a single glazed window.
To further enhance the insulation, we recommend combining double glazing with Low-E and Argon gas as the best solution. This gives a heat loss reduction of up to 70% compared to 4mm clear single glazing as it keeps the inner pane of glass warmer. Thermal spacers can further enhance performance and help reduce condensation.
Note: Double glazing does not eliminate condensation.
*Improved heat loss reduction in comparison with 4mm clear float glass. Percentages vary depending on glass combinations.

Safety and security
Safety is important and the NZ Building Code stipulates that certain sizes or locations must be able to withstand impact without breaking.
Standard safety glass will shatter rather than break. However, there are special glass types with varying penetration resistance through to bullet-resistant glass.
All UNO windows and doors comply with the NZ Building Code. For standard safety requirements, toughened or laminated glass is sufficient. Glass designed for forced entry protection is usually only selected when high security is required.
Download the UNO glass brochure to discover more about our range of available glass types and find the best solution for your upcoming project.
Get your free copy
Discover inspiration from a range of our completed projects





/Island%20Bay%20Townhouse%20-%20Living%20Room%20Wellington%20-%20Gallery%20Resized.png)









/Island%20Bay%20Townhouse%20-%20Living%20Room%20Wellington%20-%20Gallery%20Resized.png)




Test Caption Test Caption
Common glass FAQs. If you can't find the answers you're after, check out our resources page.
Explore more FAQsThere are so many glass options, how do I know what's best for my project?
addWe can help you with this, there are specific solutions for reduction of sound, fading, condensation, safety, or energy efficiency. Tell us your needs and we can give you a recommendation that will be most suited to your project.
Do you do triple glazing?
addYes we do, however this is available for the UNO Thermal range only.
Can you see the Low-E coating on glass?
addNo, the coating is virtually invisible. In some brands, the glass may appear slightly greener but usually it is very similar to clear glass.
Do you have any questions or need help choosing the perfect glass for your project?
Tell us about your project. UNO experts are experienced in working with architects, builders, and developers to ensure your vision becomes a reality.
Contact us

