In 2022, the New Zealand Building Code energy efficiency requirements were updated. This is a major step for our national standards, requiring a major adjustment for builders and suppliers.
In this article, we have outlined what the updated standards are for commercial buildings and how to meet them on your next project. If you work on housing developments or new build homes, we recommend reading our article about the requirements for residential buildings instead.
In this article, we focus on the following topics:
- Commercial building classifications
- What are the H1 Building Code standards?
- How to calculate the R-value requirements for your windows
Commercial building classifications
Building classifications are determined by the A1 Classified Uses and include housing, communal residential, communal non-residential, commercial, industrial, outbuildings, and ancillary. The commercial classification applies to a building in which natural resources, goods, services, or money are developed, sold, exchanged, or stored.
Some common examples include:
- Banks
- Car-parks
- Offices
- Restaurants
- Storage facilities
What are the H1 standards?
The New Zealand Building Code is divided into eight categories, labelled A through H, as shown below. MBIE recently updated the H1 standards for energy efficiency, increasing insulation and ventilation requirements for both residential and commercial buildings.
The standards require certain building elements, including the windows, walls, roof, and floor, to achieve a certain level of R-value.

How to calculate R-value requirements
An R-value describes how well an insulating material resists heat transfer. The higher the R-value rating, the more effective the component is at preventing thermal transfer. There are several factors that impact the R-value requirements of your commercial building, including the thermal envelope, location, window type, and building size.
Thermal envelope
To calculate the H1 requirements for your windows, you need to determine where the building’s thermal envelope is. For example, for an office block on the front of a non-insulated, unconditioned warehouse or factory, the calculation only applies to the thermal envelope around the office block itself.
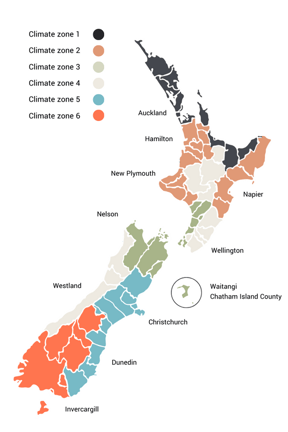
Location and climate zones
The location of your building project will affect which rules to follow, depending on the average temperature and weather patterns. Identify which of the climate zones applies to your project before proceeding to the next step.
Building size
You also need to identify the size of your commercial building. This is divided into two categories - up to 300m2 and greater than 300m2. We have explained which calculations to use for each below.
Note:
- For any of the Schedule, Calculation, & Modelling methods, UNO needs to provide the project specific ‘Construction R-value’ for the windows & doors. This allows the architect can complete the building H1 calculation in accordance with H1/AS1 or H1/AS2.
- For building elements with embedded heating systems, the minimum construction R-values shall be determined through the Schedule method. These apply whenever building elements that are part of the thermal envelope include heating systems and these R-values may not be reduced by applying the Calculation method.
Small commercial buildings (up to 300 sqm)
For small commercial buildings, your calculation method will depend on the window type used and the relevant climate zone. Start by asking the following question:
Where is your building site?
The location of your building project will affect which rules apply to you, depending on the average temperature and weather patterns. Identify the climate zone your project is located in before proceeding to the next step. See section above on Location and climate zones.
Has your building got a curtain wall?
If yes, you will need to use the Modelling method, as outlined below. If not, you can use the following methods in H1/AS1, Schedule, Calculation, or Modelling – refer to additional notes on these methods below.
Schedule method
If the glazing area of your small commercial building is less than 30% of the total wall area , you may use the scheduling method.
- Identify the R-value requirements for your climate zone.
- Send your plans to UNO Windows & Doors. We will supply the construction R-value report along with certification to assist with your compliance with the Building Code.
- Each component must comply with the minimum R-value as stated in H1/AS1 2.1.2.
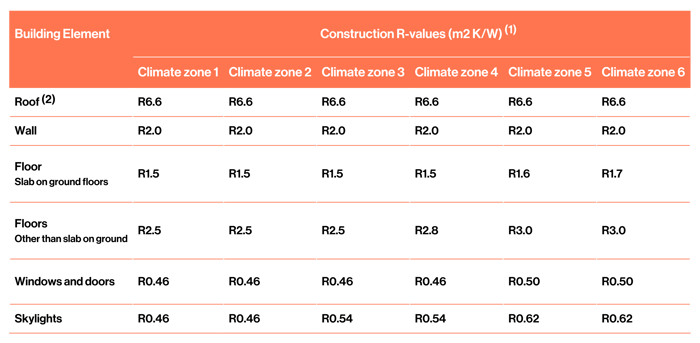
If the building has an embedded heating system, refer to H1/AS1 2.1.2.2a. However, most commercial buildings do not have embedded heating systems so we have supplied the table below to show common construction R-value requirements for buildings under 300 sqm.
TABLE 2.1.2.2B: Minimum construction R-values for building elements that do not contain embedded heating systems
Paragraph 2.1.2.2 b)"
NOTES:
(1) Climate zone boundaries are shown in Appendix C.
(2) In roofs with a roof space where the insulation is installed over a horizontal ceiling, the roof R-value may be reduced to R3.3 for a distance of up to 500 mm from the outer edge of the ceiling perimeter where space restrictions do not allow the full-thickness of insulation to be installed.
(3) For building consent applications submitted before 2 November 2023, the minimum construction R-values for windows and doors in climate zones 1 and 2 are permitted to be reduced to R0.37 m²·K/W."
Calculation method
If the glazing area of your small commercial building is less than 40% of the total wall area, you may use the Calculation method.
- Refer to H1/AS1 section 2.1.3, NZBCH1, or the BRANZ calculator tool.
- Send your plans to UNO Windows & Doors. We will supply the construction R-value report along with certification to assist with your compliance with the Building Code.
For buildings up to 300sqm, you can also use the tool from the NZBC online calculator to input the square metre areas and construction R-values of each component. This will advise you of the heat loss from your building compared to the reference building and if you are compliant with the new standards.
This lets you play with the insulation numbers and gives you the ability to adjust and reduce insulation R-values in other areas, potentially reducing construction costs. See our previous blog post about how to achieve the ideal R-values for an example of how savings can be obtained.
Note: The minimum R-value for the floor, wall or roof using the Calculation method is 50% of the Schedule method R-value for that building element.
Modelling method
For projects that cannot be calculated according to the Schedule method or Calculation method, use the Modelling method.
- Refer to H1VM1 Appendix D.
- Identify the construction R-values for the vertical windows and doors, opaque doors, and the solar heat gain coefficient for any glass in the proposed thermal envelope.
- Send your plans to UNO Windows & Doors. We will supply the construction R-value report along with the solar heat gain coefficient and certification to assist your compliance with the code.
Large commercial buildings (more than 300 sqm)
Similarly to smaller buildings, the method for commercial buildings greater than 300 sqm depends on the window type used and the relevant climate zone. Start by asking the following questions:
Where is your building site?
The location of your building project will affect which rules apply to you, depending on the average temperature and weather patterns. Identify the climate zone your project is located in before proceeding to the next step. See section above on Location and climate zones.
Has your building got a curtain wall?
If yes, you will need to refer to VM2 clause E3 method for the building H1 calculation which is the Modelling method, as outlined below. If no, you can use the following methods in H1/AS2, Schedule, Calculation, or Modelling – refer to additional notes on these methods below.
Schedule method
For any large building with a glazing area less than 50% of the total wall area, you may use the Schedule method.
- Identify the R-value requirements for your climate zone.
- Send your plans to UNO Windows & Doors. We will supply the construction R-value report, as well as certification to assist with your compliance with the Building Code.
- Each component must comply with the minimum R-value stated in H1/AS2 2.1.2.
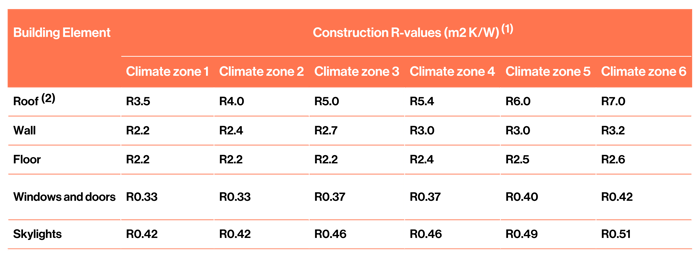
If the building has an embedded heating system, refer to H1/AS1 2.1.2.2a. However, most commercial buildings do not have embedded heating systems so we have supplied the table below to show common construction R-value requirements for buildings greater than 300 sqm.
TABLE 2.1.2.2B: Minimum construction R-values for building elements that do not contain embedded heating systems
Paragraphs 2.1.2.2 b), 2.1.3.11
NOTES:
(1) Climate zone boundaries are shown in Appendix C.
(2) In roofs with a roof space, where the insulation is installed over a horizontal ceiling, the roof R-value may be reduced to R3.3 for a distance of up to 500 mm from the outer edge of the ceiling perimeter where space restrictions do not allow full-thickness insulation to be installed.
Calculation method
To use this method, the solar aperture must be less than or equal to 0.5. See clause H1/AS2 2.1.3.2.
- Refer to H1/AS2 section 2.1.3, or the BRANZ calculator tool.
- Send your plans to UNO Windows & Doors. We will supply the construction R-value report, as well as the solar heat gain coefficient and certification to assist with your compliance with the Building Code.
Please note that this method does not allow for a reduction of the R-value in the roof, floor or skylights. However, it does allow you to adjust and reduce insulation R-values in other areas, potentially reducing construction costs.
Modelling method
For projects that cannot be calculated according to the Schedule method of Calculation method, use the Modelling method.
- Refer to H1VM2 appendix D.
- Identify the construction R-values for the vertical windows and doors, opaque doors, and the solar heat gain coefficient for any glass in the proposed thermal envelope.
- Send your plans to UNO Windows & Doors. We will supply the construction R-value report, as well as the solar heat gain coefficient and certification to assist your compliance with the code.
Window experts NZ
Calculating the requirements for your new project can be complicated, especially with these new H1 standards. To reduce the stress, streamline the planning phase, and ensure your project is compliant, we suggest speaking with our team early in the design process.
When you have concept plans - with elevations, floor plans, and a window schedule - we can advise the window profile and glass to suit your design and the H1 insulation requirements.




